Catalog
Recently Viewed
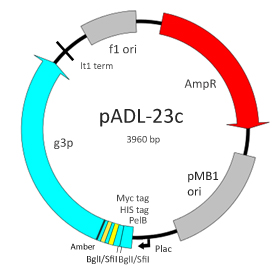
pADL-23c
Technical Description
pADL™-23c is a phagemid vector designed for phage display on the N-terminal side of the protein III of the filamentous bacteriophage M13 or equivalent. This vector contains a PelB leader sequence for expression in the periplasm, a double-SfiI cloning site to introduce scFvs or Fab fragments, a HIS tag for purification, a Myc tag for detection and an amber codon located before the full-length copy of the gene III sequence. On non-suppressive bacterial strains, free scFvs or Fab fragments are produced in the periplasm where they can be assayed for binding or purified for further testing. Expression of the fusion is under the control of a lac promoter that has been adjusted at a level comparable to the widely used phagemid pCOMB3.
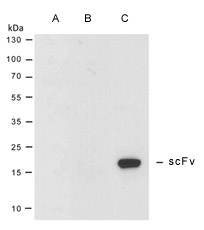
Figure 1. Binding of Myc tag antibody to HyHEL-10 scFv. Western blot analysis of periplasmic extracts prepared from varied phagemids containing the HyHEL-10 scFv insert. Only the scFv derived from pADL-23 exhibits a strong reactivity with a Myc tag antibody (Lane A: pADL-20, Lane B: pADL-22, Lane C: pADL-23).
Applications
-
Phage display at the N-terminal side of gene III protein of the filamentous bacteriophage.
-
Free scFv or Fab expression.
For research use only; not intended for any animal or human therapeutic or diagnostic use.
Specifications
General Characteristics:
Plasmid Size: 3960
Promoter: lac promoter
Leader Peptide: PelB
Cloning Site: double-BglI/SfiI, NotI-SpeI
Purification: HIS tag
Detection: Myc tag
Fusion Protein: full length gene III protein and conditional Amber stop codon
Selection: ampicillin
Replication: oriF1, pMB1
Physical Characteristics:
Concentration: 0.5 µg/µl.
Product Size: 10 µg.
Buffer: DNA Conservation Buffer (Tris/HCL 5 mM, EDTA 0.1 mM, pH 8.5, sterile).
Storage Temperature: -20°C.
Quality Control & Certification of Analysis
Product Size:
Digestion by EcoRI and NheI generates 2 fragments of 2.6 kb and 1.4 kb.
Product Sequence:
Complete vector sequence is analyzed.
Certification:
Product meets all specifications.

Citations
-
Jiang Y, Lin Y, Krishnaswamy S, Pan R, Wu Q, Sandusky-Beltran LA, Liu M, Kuo MH, Kong XP, Congdon EE, Sigurdsson EM (2023). Single-domain antibody-based noninvasive in vivo imaging of α-synuclein or tau pathology. Sci. Adv.,9(19):eadf3775.
-
Mikolajek H, Weckener M, Brotzakis ZF et al. (2022). Correlation between the binding affinity and the conformational entropy of nanobody SARS-CoV-2 spike protein complexes. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A.,119(31):e2205412119.
-
Akkermans O, Delloye-Bourgeois C, Peregrina C et al. (2022). GPC3-Unc5 receptor complex structure and role in cell migration. Cell,185(21):3931-3949.
-
Jester BW, Zhao H, Gewe M, Adame T. et al. (2022). Development of spirulina for the manufacture and oral delivery of protein therapeutics. Nat. Biotechnol.,40(6):956-964.
-
Löbel M., Salphati S.P., El Omari K., Wagner A., Tucker S.J., Parker J.L., Newstead S. (2022). Structural basis for proton coupled cystine transport by cystinosin. Nat. Commun.,13(1):4845.
-
Jester BW, Zhao H, Gewe M et al. (2022). Development of spirulina for the manufacture and oral delivery of protein therapeutics. Nat Biotechnol., Mar 21.
-
Melia C.E., Bolla J.R., Katharios-Lanwermeyer S., Mihaylov D.B., Hoffmann P.C., Huo J., Wozny M.R., Elfari L.M., Böhning J., Morgan A.N., Hitchman C.J., Owens R.J., Robinson C.V., O'Toole G.A., Bharat T.A.M. (2021). Architecture of cell-cell junctions in situ reveals a mechanism for bacterial biofilm inhibition. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A., 118(31):e2109940118.
-
Gomez-Castillo L., Watanabe K., Jiang H., Kang S., Gu L. (2020). Creating Highly Specific Chemically Induced Protein Dimerization Systems by Stepwise Phage Selection of a Combinatorial Single-Domain Antibody Library. J Vis Exp. , 14;(155):10.3791/60738.
-
Mendoza-Salazar I., Gómez-Castellano KM., González-González E., Gamboa-Suasnavart R., Rodríguez-Luna SD., Santiago-Casas G., Cortés-Paniagua MI., Pérez-Tapia SM., Almagro JC. (2022). Anti-SARS-CoV-2 Omicron Antibodies Isolated from a SARS-CoV-2 Delta Semi-Immune Phage Display Library. Antibodies (Basel),10;11(1):13.
-
Maeda S., Xu J., N Kadji FM., Clark M.J., Zhao J., Tsutsumi N., Aoki J., Sunahara R.K., Inoue A., Garcia K.C., Kobilka B.K. (2020). Structure and selectivity engineering of the M1 muscarinic receptor toxin complex. Science,369(6500):161-167.
-
Huo J., Le Bas A., Ruza RR. et al. (2020). Neutralizing nanobodies bind SARS-CoV-2 spike RBD and block interaction with ACE2. Nat Struct Mol Biol., 27(9):846-854.
-
Gomez-Castillo L., Watanabe K., Jiang H., Kang S., Gu L. (2020). Creating Highly Specific Chemically Induced Protein Dimerization Systems by Stepwise Phage Selection of a Combinatorial Single-Domain Antibody Library. J. Vis. Exp. (155), e60738.
-
Huen J., Yan Z., Iwashkiw J., Dubey S., Gimenez M.C., Ortiz M.E., Patel S.V., Jones M.D., Riazi A., Terebiznik M., Babaei S., Shahinas D. (2019). A Novel Single Domain Antibody Targeting FliC Flagellin of Salmonella enterica for Effective Inhibition of Host Cell Invasion. Front Microbiol., 10,2665.
-
Hassan K.M.A., Hansen J.D., Herrin BR, Amemiya C.T. (2019). Generation of Lamprey Monoclonal Antibodies (Lampribodies) Using the Phage Display System. Biomolecules, 9(12), 868.
-
Valadon P., Pérez-Tapia S.M., Nelson R.S., Guzmán-Bringas O.U., Arrieta-Oliva H.I., Gómez-Castellano K.M., Pohl M.A., Almagro J.C. (2019). ALTHEA Gold Libraries™: antibody libraries for therapeutic antibody discovery. MAbs, 11(3):516-531.
-
WIPO Patent Application (2017). Vectors for cloning and expression of proteins, methods and applications thereof. WO 2017/175176 A1.
-
WIPO Patent Application (2016). Anti-salmonella Antibodies And Uses Thereof. WO 2016/125089 A1.



